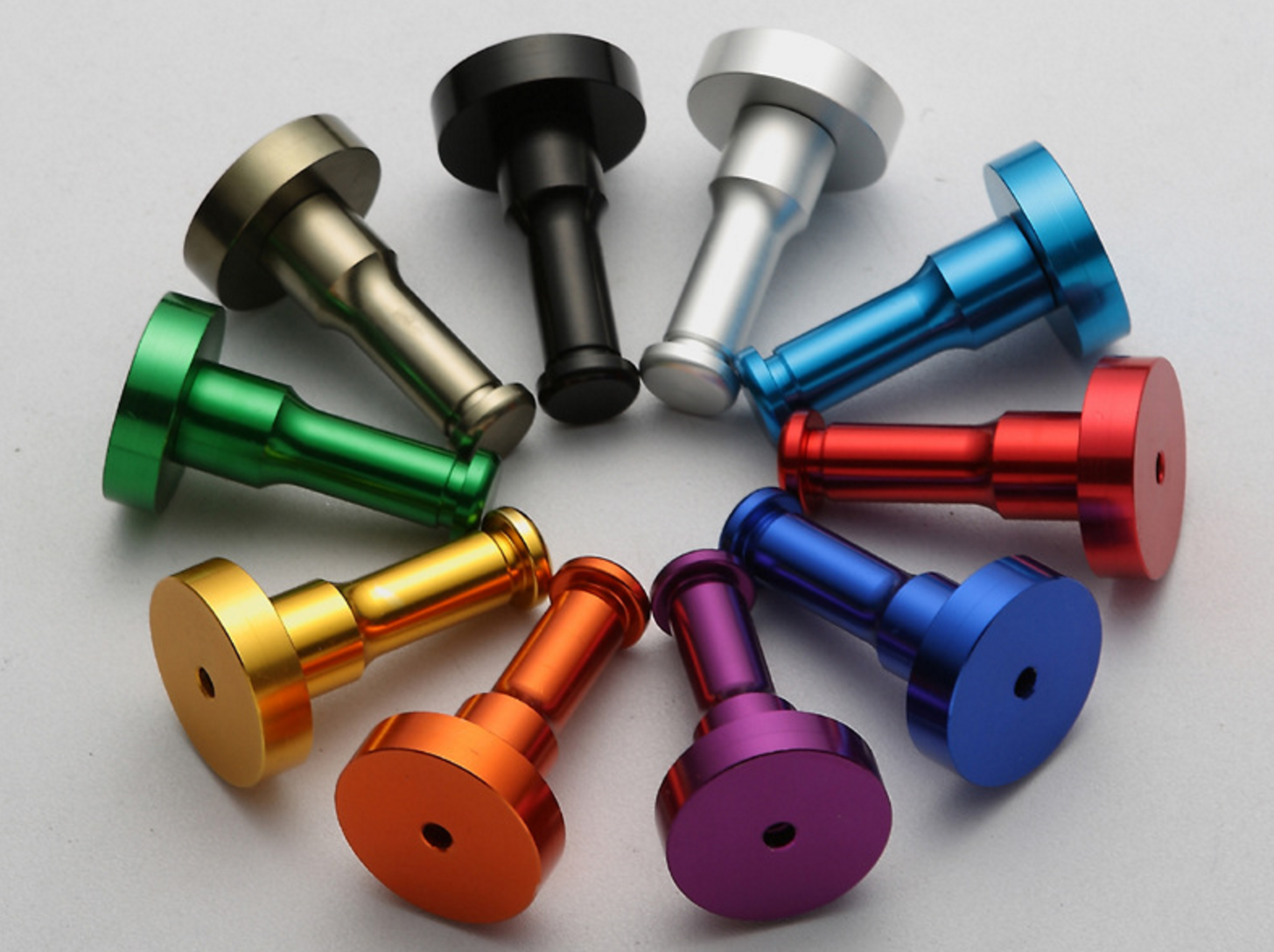


Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a decorative, durable, corrosion-resistant, anodic oxide finish. Hard Anodizing (type III) is due to the fact that hardcoating imparts a very hard, dense, abrasion-resistant oxide on the surface of the aluminum
✓ Anodic coatings are highly abrasion-resistant an durable
✓ Anodic coatings are resists corrosion
✓ Anodic coatings do not peel, chip,etc.
✓ Anodic coatings are translucent, resulting in a deep, rich metallic appearance
✓ Anodic coatings are scarcely affected by sunlight
✓ MIL-1-8625 TYPE I,II AND III, CLASS 1 & 2
✓ AMS 2469 HARD ANODIC COATING
✓ AMS 2470 CHROMIC ACID ANODIC COATING

Chem Film, is a chemical conversion coating that is used to passivate aluminum. Chem Film is applied by dipping, spraying or brushing
✓ It protects aluminum substrates from corrosion
✓ The bonding of paint, lacquer, and organic finishes to chromate conversion coating is excellent
✓ The dimensions unchanged
✓ Anodic coatings are translucent, resulting in a deep, rich metallic appearance
✓ Anodic coatings are scarcely affected by sunlight
✓ MIL-C-5541E CLASS 1A & CLASS 3
✓ MIL-DTL-5541 TIPO I & TIPO II, CLASS 1A & CLASS 3

Is the process of covering substrate metals (like steel and iron, etc.) with a layer or coating of zinc to protect the substrate from corrosion
✓ It protects substrates from corrosion
✓ Zin metal platings is preferred for those who also aim for aesthetics
✓ ASTM B 633 SC1, SC2, SC3, SC4 & Type I, II, III, IV, V, VI
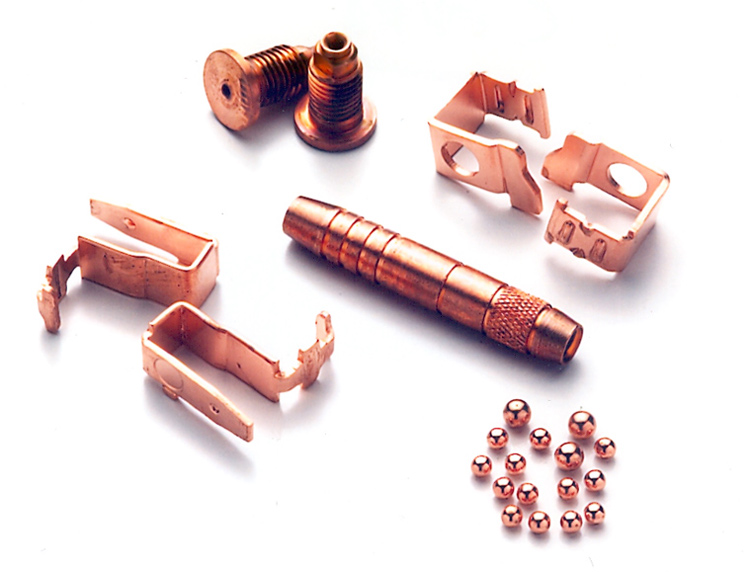


Used typically to provide an anti-seize surface, to prevent carburizing of surfaces on which carburizing is neither required or permitted, to prevent decarburization, to enhance solderability, or to provide a source of copper for furnace brazing. They are used in printed circuits, electronics, semiconductor, rotogravure, electroforming, decorative, and plating on plastics.
✓ Good solderability
✓ Excellent conductivity
✓ Good corrosion when used as the first layer
✓ Inhibits electromagnetic interference with a thickness of 1 mm plating
✓ It is used as a sub-plate to promote the adhesion of veneers in zinc diecasts
✓ AMS2408 Type 1 & 2

The commercial application of black conversion coating to iron, steel, stainless steel and cast iron has been well established for over 75 years. The three most economically viable methods of blackening ferrous alloys are chosen for a number of reasons.
✓ They produce an attractive black finish that enhances the saleability of the articles thus coated
✓ They offer an economical means of imparting moderate corrosion resistance to the articles thus coated
✓ They yield a finish that when properly sealed resist galling and enhances lubricity
✓ These finished yield little or no dimensional change
✓ Black oxide coating are used on munition cases and gun barrels.
✓ These coatings are particularly suited for moving parts that cannot tolerate the dimensional build up of a more corrosion resistant finish.
✓ Decorative purposes
✓ Decrease in light reflection
✓ MIL-DTL-13924 CLASS 1, 2 & 4

Passivation is the formation of a relatively inert film on the surface of a material (often a metal), which masks it against the action of external agents.
Advantages✓ Dissolve tramp metallic elements from the surfaces or corrosion resistant steels to improve their corrosion resistance.
Applicables Standars✓ ASTM A967 Nitric & Citric
✓ AMS2700 Method 1 and Method 2


The chromium metal electrodeposited is extremely hard and corrosion resistant. It has a low coefficient of friction and imparts exceptional wear characteristics to parts on which it is plated. This process is generally used to give deposit thicknesses of >0.1 mil (2.5 um) and up to 20 mils (500 um) or more. Functional chromium is also used to rebuild or salvage worn parts such as rolls and roll journals, molding, dies, and other tools, cylinder liners, crankshafts, and mismachined items.
✓ To increase wear and abrasion resistance
✓ To increase fretting resistance
✓ To reduce static and kinetic friction
✓ To reduce galling or seizing, or both, for various metal combinations✓ To increase corrosion resistance
✓ To build up undersize or worn parts
✓ Class 1 plating is applied as a decorative finish
✓ ASTM B650 Class 1 & Class 2
✓ QQ-C-320 Class 1 & Class 2, Type I and II
✓ AMS 2460

Tin and tin-lead alloys are solderable and, therefore, are used extensively in the electronics industry to bond electronic components. Tin and tin-lead electroplating solutions are used to plate components in numerous engineering, communications, military, and consumer product applications.
✓ Good solderability and reflowability.
✓ Low porosity
✓ Good corrosion resistance
✓ Use as a base for soldering printed circuity and microwave parts and components
✓ Tin-lead plating intended for used as a coating for corrosion protection and a base for soldering
✓ MIL-T-81955 Class 1,2,3 & 4
✓ AMS-P-81728
✓ ASTM B545

Nickel electroplating is one of the most versatile surface-finishing processes available having a broad spectrum of end uses that encompass decorative, engineering, and electroforming applications. The coatings are protective, mirror- bright, and smooth.
Advantages✓ Use to protect iron, copper, or zinc alloys against corrosive attack.
✓ Decorative purposes
✓ Used for wear resistance
✓ Abrasion resistance
Applicables Standars✓ AMS-QQ-N-290 Class 1 & Class 2

The part is manufactured of the nonconductor and the metal added to its significant surfaces to impart specific metallic properties.
Typical examples of this are:
✓ For strength
✓ For electrical conductivity
✓ For metallic appearance, as in the metallizing of buttons, drawer pulls, door knobs, automotive and appliance hardware, toys, etc. made of plastic.